Tonsillitis
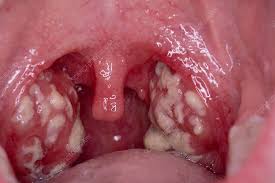
Inflammation of the tonsils. Tonsils are balls of lymph tissue on both sides of the throat, above and behind the tongue. They act as filters, trapping germs that could otherwise enter the airways and cause infection. They also produce antibodies to fight infection. Tonsils can sometimes get inflamed when affected by bacteria or viruses; when they swell and get inflamed, it is known as tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis is common, especially among children. The condition can occur occasionally or frequently. When a person infected with bacteria or virus breathes, coughs or sneezes nearby, the infection can spread to others around through air droplets, causing tonsillitis. The main symptom of tonsillitis is a sore throat. The throat and tonsils usually look red and swollen. The tonsils may have spots or pus that covers them completely or in patches. Fever is also common. Tonsils are normally large during childhood, but they can cause trouble when they get infected or grow too large.