Multiple Myeloma
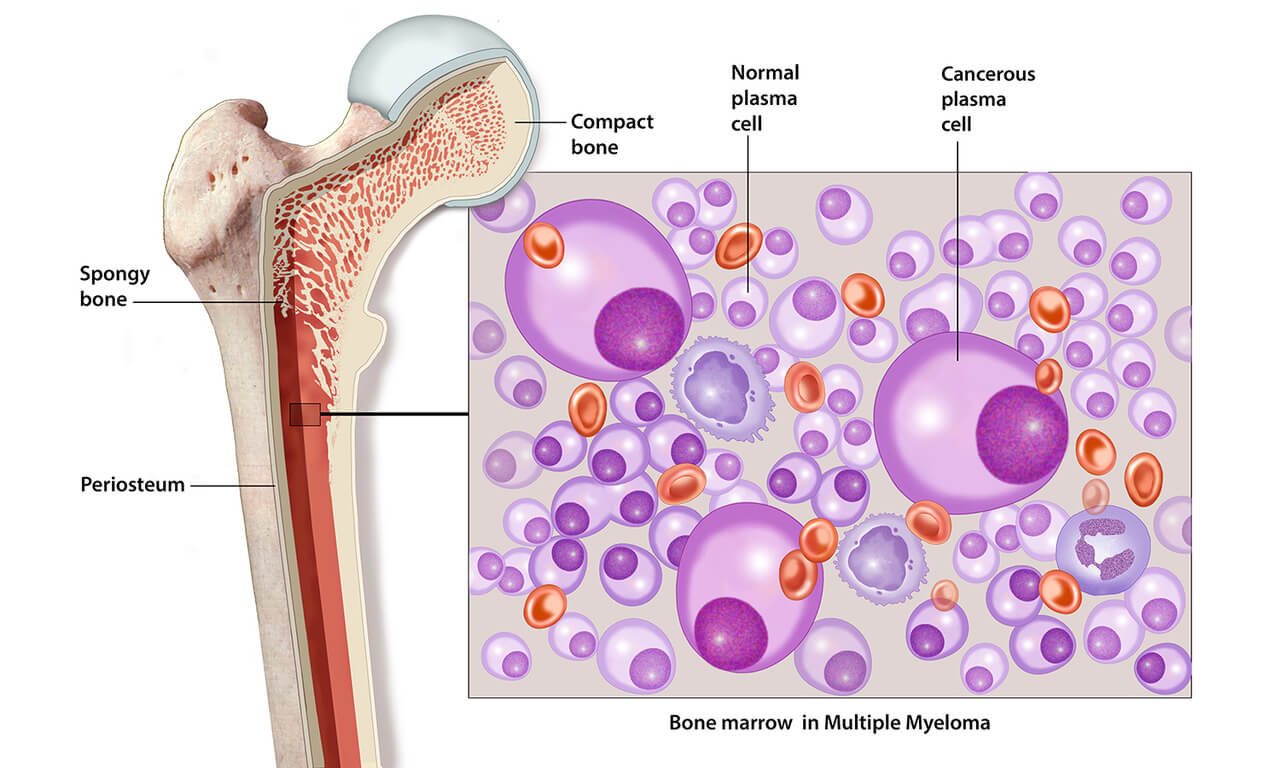
Multiple Myeloma is a malignant or cancerous condition of the plasma cells of the blood. It is also called Plasma cell Myeloma. The word Myeloma pertains to the cells of bone marrow. The bone marrow is a soft substance within the bones which manufacture all kinds of blood cells. The basic cells are called stem cells. Some of the stem cells develop into small white cells, also called Lymphocytes. The lymphocytes are of two types, B Lymphocytes and T Lymphocytes. (They are also called B cells and T cells). The B cells, further grow into Plasma cells, when the foreign substance (antigen) or bacteria enter the body, the B cells develop into Plasma cells to form what is called as Immunoglobulins (antibodies), to fight against the antigens or infections. The Immunoglobulins are denoted as Ig, which are of five major types: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD and IgE.
In short, the plasma cells have the capacity to turn into the Immunoglobulins (Ig), as a part of the defence mechanism of the body. These plasma cells when turning cancerous, it is called Multiple Myeloma. These cancerous plasma cells keep multiplying rapidly and travel in the bloodstream, damaging body tissues. The malignant plasma cells produce too many (multiple) Immunoglobulins which are actually not required by the body. This entire condition is called Multiple Myeloma.
Multiple Myeloma is nothing but the cancer of the plasma cell, an important part of the immune system that produces immunoglobulin (antibodies) to help fight infection and disease. Unchecked overgrowth of these cells leads to multiple tumours and lowered immunity. The tumours invade the hard surface of the especially the large bone, spreading into the cavities of the bones.
Multiple Myeloma is the second most common blood cancer, after Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas. About 13000 new cases of MM are reported every year in the US. It is relatively more common amongst the Americans versus their Asian counterpart. It is more common in men, after 60 years of age.
The exact cause for MM is not yet clearly understood. The common factors influencing the development of MM are genetic tendency, radiation, chemicals (herbicides, insecticides, petroleum products, heavy metals, plastics), and virus.
The clinical symptoms often are vague or no symptoms in the early stage of MM. Some of the presenting symptoms are:
- Severe lower back pain or rib pain
- Anaemia and lowered immunity leads to weakness and tendency to frequent infections, as the production of Immunoglobulins is disturbed.