Alopecia Areata
Alopecia Areata ('baldness in spots') is a form of hair loss, usually from the scalp, although it can affect other areas of the body. The hair loss mostly remains limited to the scalp but in certain cases, it can extend to eyebrows, eyelashes, facial hair (beard, moustache), nasal hair and give rise to bald spots anywhere in the body. Alopecia Areata is a common condition which arises largely due to a mix of immunological and hormonal factors.
Alopecia Areata is considered to be an auto-immune condition in which the immune system of the body (which protects the body from bacteria and viruses) mistakenly attacks the hair follicles and destroys them. This leads to hair loss in the affected area.
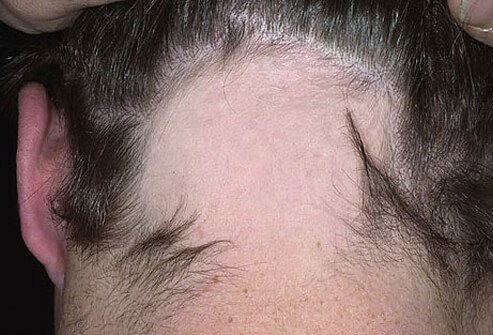
The commonest presentation of Alopecia Areata is the appearance of bald patches on the scalp. In most cases, hair falls out in small, round patches about the size of a small coin. The patient may have single or multiple such patches. In some cases, these patches may remain static, whereas in some cases the patches may spread to involve larger areas of the scalp. In some cases, hair loss is more extensive. Although it is not very common, the disease can progress to cause total loss of hair on the head (Alopecia Areata totalis) or complete loss of hair on the head, face, and rest of the body (Alopecia Areata Universalis).